1. What is Frie's rearrangement? write an example ?
- Frie's rearrangement is an organic rearrangement reaction in which an aryl ester is transformed into a hydroxy aryl ketone with the help of a Lewis acid catalyst and an aqueous acid. In this reaction, an acyl group belonging to the phenolic ester migrates to the aryl ring.
Example:
2. Define Diazocoupling reaction with Example ?
- Diazocoupling is an organic reaction between a diazonium compound and another aromatic compound that produces an diazo compound
Example :
3.Write the Hoffman rearrangement
- The Hoffman rearrangement is an organic reaction used to convert a primary amide to a primary amine using a halogen, base,water and heat
4. Define and Classify Carbonion with example ?
- A Carbanion is an anion in which carbon is trivalent and bears a formal negative Charge.
Example: Methide ion, methyl anions, phenyl anion
Classification: 1 Methone Carboanion
2 Primary Carboanion
3 Secondary Carboanion
4 Tertiary Carboanion
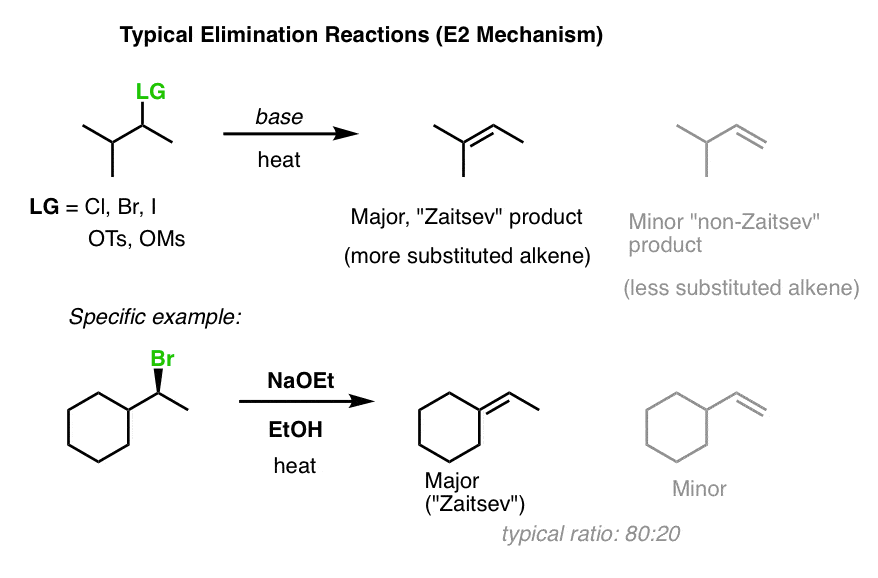
5. State Saytzeff's rule?
-The rule may be stated in two ways:
1 the most substitute alkene is the predominant product i.e, the C═C with largest with largest number of alkyl substituent is formed.
2. Hydrogen is eliminated preferentially from the carbon atom joined to the least number of hydrogen atoms.
6.Write the Chlorination of methane ?
- If a mixture of methane and chlorine is exposed to a flame it explodes-producing Carbon and hydrogen chloride . This is not a very useful reaction! the reaction we are going to explore is a more gentle one between methane and chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light-typically sunlight. This is a good example of a photo-chemical reaction brought about by light.
CH4(g) + Cl2(g)⟶ CH3Cl(g) + HCl(g)
7. Outline the generation of free radical?
- Free radicals are natural by-product of aerobic cell metabolis. They are produced by a number of actions including infections, disease and lifestyle. The generation can be endogenous. The exogenous source of free radical is from the environment.
8. Define Metamarism with example?
- Metamerism is a type of isomerism which is due to the unequal distribution of carbon atoms on either side of a functional group. Metamers belong to the same homologous series, for example diethyl ether and methyl propyl ether.
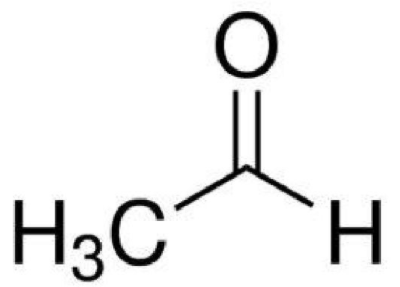
9.Write the structure and IUPAC name i)Formic acid ii) Neopenten
- i)Formic acid : Structure
IUPAC Name: Methanoic acid
ii) Neopenten: Structure
IUPAC name: 2,2-dimethylpropane
10. Write the structure - a) Acetanilide b) Acetophenone
- Acetanilide : 
Acetophenone
11. Write smith reaction with example?
- Simmons-Smith reaction is an asymmetric reaction in which a carbenoid adds to an alkene or alkyne to form a cyclopropane. It is an essential reaction involving an organozinc reagent.
For example, both butene and cyclohexene will undergo this reaction
12. Outline the Gatterman reaction with example?
- Gatterman reaction is formylation method of aromatic ring compounds, The benzene is added with Hydrocyanic acid and Friedl craft's catalyst AlCl₃ to form benzene diazonium choloride which on further hydrolysis produces as aldehyde. In such reaction copper acts as catalyst.
13.Write the possible resonance structure of Phenoxide ion?
14. Define Hofmann's Elimination with example?
-Hofmann elimination is the process of creating tertiary amines and alkenes from the treatment of quaternary ammonium with excess methyl iodide, and the treatment of the resulting compound with silver oxide, water and heat. Example: silver hydroxide
15. Write the stability of free radicals with example ?
- If the internal energy of the radical is low. The radical is stable. It will have little tendency to react further. Free radicals have only 7 electrons inn their Valence shell. They are higher in energy than atoms with 8 valance electrons
16.Define Homolytic bond breaking with example ?
- Homolytic clevage is the breaking of a covalent bond in such a way that each fragment gets one of the share electrons. The word homoios, "equal". and lysis "looseing".
example: The homolytic cleavage of a Br-Br bond is Homolytic cleavage produces free radicals.
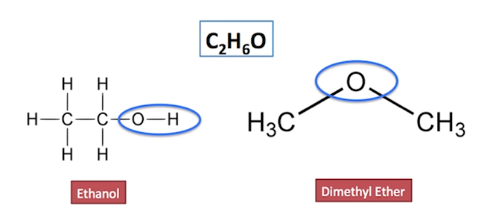
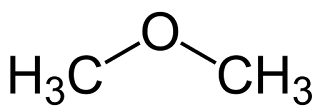
17.Why ethanol is higher boiling point than the dimethyl ether ?
- The ethanol has a much higher boiling point than the dimethyl ether because the viscosity of ethanol is greater than that of ether because there in H bonding in alcohols in alcohols leading to higher force of bonding.
18. Write the structure and IUPAC name of : a) Isopropyl alcohol, b) Ethyl acetoacetate
- a) Isopropyl alcohol:-
b) Ethyl acetoacetate
19. What is Williamson's synthesis? Give an example?
- The Williamson ether synthesis is an organic reaction, forming an ether from an organohalide and a deprotonated alcohol. This reaction was developed by Alexander Williamson in 1850. Typically it involves the reaction of an alkoxide ion with a primary alkyl halide via an SN2 reaction
An example is the reaction of sodium ethoxide with chloroethane to form diethyl ether and sodium chloride:
[Na]+[C2H5O]− + C2H5Cl → C2H5OC2H5 + [Na]+[Cl]
20. Write structure of Cis and Trans-2-butene?
-
21.What is Diazotization Reaction with Example ?
- Aromatic amine reacts with nitrous acid and mineral acid to form diazonium salt and produces water as a side product. This reaction is known as Diazotization Reaction.
example: aniline with sodium nitrate and HCl at the temperature of 273K
22.Define and classify nitrenes?
- In chemistry, a nitrene or imene is the nitrogen analogue of a carbene. The nitrogen atom is uncharged and univalent, so it has only 6 electrons in its valence level—two covalent bonded and four non-bonded electrons.
-Instead, they are formed as reactive intermediates during a reaction. There are two common ways to generate nitrenes: from azides by thermolysis or photolysis, with expulsion of nitrogen gas. This method is analogous to the formation of carbenes from diazo compounds.
23.Write the stability of Carbanion?
- The stability order of carbanion decreases, while moving from primary to the tertiary anion, due to increase intensity of negative charge on central carbon of tertiary anion.
24. Write the difference between E1 and E2 reaction?
-
| E1 |
E2
|
| solvent act as base |
solvent base required |
| Two Step Process |
One Step Process |
| First order kinetics |
Second order kinetics |
|
Reactivity order
3∘>2∘>1∘
|
Reactivity order
3∘>2∘>1∘
|
| Follows Saytzeff's rule |
Follows Hofmann's rule |
| Carbocation is formed |
Transition state |
| Non-stereo specific and non-stereoselective |
stereoselective and stereo specific |
| Polar solvent increase the rate if reaction |
Polar solvent decrease the rate of reaction |
25.What is Free radical substitution reaction?
-These are reactions in which one atom in a molecule is replaced by another atom or group of atoms. Free radical substitution often involves breaking a carbon-hydrogen bond in alkanes.
Example:- The reaction between methane and chlorine in the presence of UV light.
26.Classify free radicals with examples?
27. Define functional and positional isomerism with example?
-Functional:- The functional isomerism arises due to different functional groups. The functional isomerism have same molecular formula but different functional groups.
example:-
Positional:- The positional isomerism arise due to different position of side chains constituents functional groups, double bond, triple bond etc. on the parent chain.
example:-
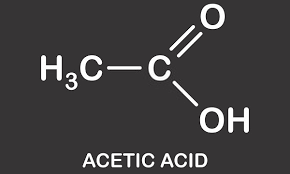
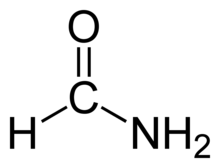
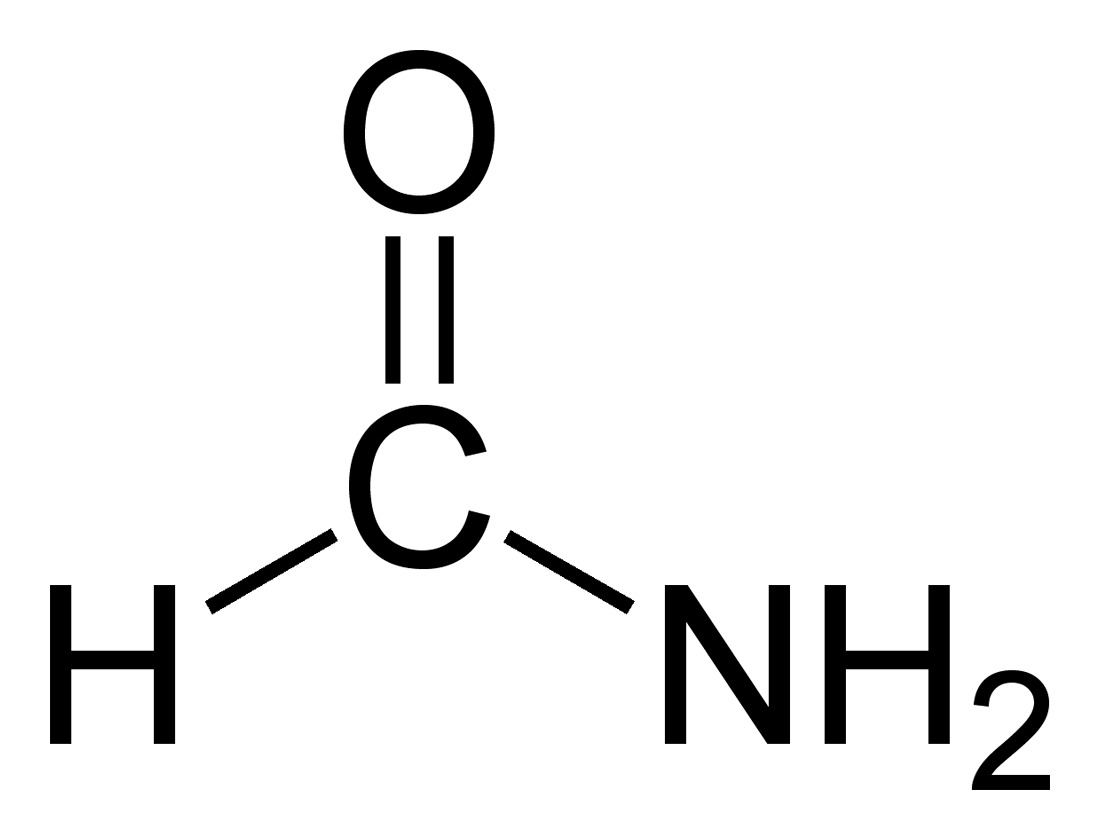
28.Write the structure and IUPAC name :- a) Acetic acid b)Formamide
- a) Acetic acid:-
IUPAC Name:- Ethanoic acid
b) Formamide:-
IUPAC Name:- Formamide Methanamide
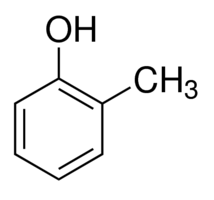
29. Write the structure of - a) Aniline b) O-cresol
- a) Aniline:-
IUPAC Name:- Phenylamine
b) O-Cresol:-
IUPAC Name:- 2-Methylbenzenol
30.Write the structure of- a) 2-bromo 3 methyl hexane b) Methanol
- a)
2-bromo 3 methyl hexane b) Methanol :-
31.Define and Classify hydrogen bond with example?
- A weak bond between two molecules resulting from an electrostatic attraction between a proton in one molecule and an electronegative atom in the other.
there are two type of H-bonds
1. Intermolecular Hydrogen bonding - example Hydrogen bonding in water, alcohol
2. Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonding
32. Write any one method for formation of free radicals with example?
-Free radicals are formed from molecules via the breakage of a chemical bond such that each fragment keeps one electron, by cleavage of a radical to give another radical and also via redox reactions
33.What is crossed Aldol condention reaction?
- In presence of an aldehyde or ketone combine with each other to from
α,β hydroxy aldehyde or ketone.
|
34.Why aliphatic amines are more basic than aromatic amines?
- In aromatic amines, the -NH2 group is attached to a -C6H5 group, which is an electron with drawing group. So, the availability of a lone pair of electrons on N is decreased.
35.What is Sandmeyer's reaction?
- The Sandmeyer reaction is a chemical reaction used to synthesize aryl diazonium salts using copper salts as reagents or catalysts.
36. Write the effects of substitution on acidity of phenols?
-The effect of electron donating groups on a phenols to make it less acidic. However, if an electron withdrawing group on the ring can further delocalized the negative charge then the anion is more stable and the phenol more acidic.
37. Write the structure and IUPAC name of a)Acetone b) Diethyl ether
-Acetone:-
IUPAC Name:- Propane
Diethyl ether:-
IUPAC Name: Ethoxyethane.
38. What is Beckmann's rearrangement?
-The Beckmann rearrangement, named after the German chemist Ernst Otto Beckmann, it is a rearrangement of an oxime functional group substituted amides.
39. Arrange the order of basicity of Aniline, Trimethyl amine, Methyl amine ,give reason?
- Trimethyl amine> Methyl amine> Aniline
Reason:- Base on the CH3 group.
40.What is Knoevengels condensation?
- The knoevenagel reaction is a modified Aldol condensation with a nucleophilic addition between an aldehyde or ketone and an active hydrogen compound in the presence of basic catalyst.
41. Define and classify Carbenes?
- A Carbene is a molecule containing a neutral carbon atom with a valance of two unshared valanced electrons
-Carbenes can be classified as - Nucleophilic, Electrophilic or Ambiphilic
42.Write the stability order of free radicals?
- Stability of free radicals increase in the order methyl<primary<secondary<tertiary
43.Write the Structure and IUPAC Name a)Ethyl Methyl Ketone b) Dimethyl ether
-a) Ethyl Methyl Ketone
IUPAC Name : Butane-2One
b) Dimethyl ether
IUPAC Name: Ethoxy Ethane
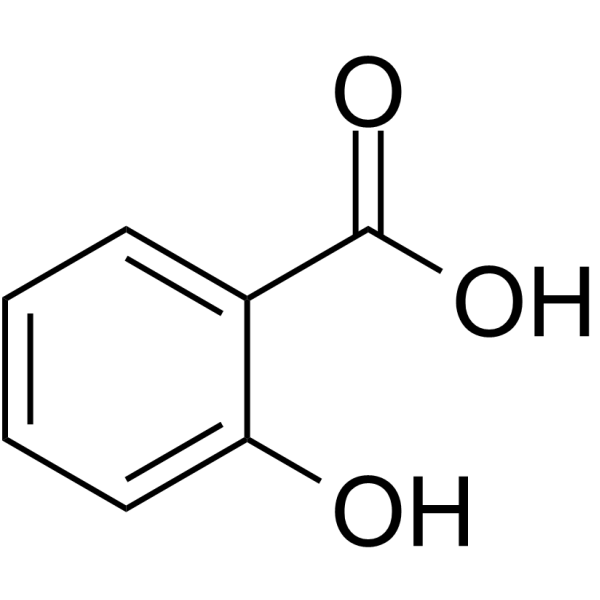
44. Write the structure of- a) Ethyl acetate, b) Salicylic acid
-A)Ethyl acetate:
45. What is Kolbe's reaction?
-Kolbe's reaction is a carboxylation chemical reaction that process by heating sodium phenoxide with carbon dioxide under pressure. then treating the product with sulfuric acid.
46.Write the effects of substituents on basicity of aliphatic amines?
- Electron withdrawing groups like F, Cl, NO2 etc. tend to attract the lone pair of nitrogen atom toward them which decrease the electron density on nitrogen atom which in term decrease the basicity of amines.
Electron realising groups increase the electron density on nitrogen atom which increase the basicity of amines.
47.Write the bromination of methane?
- It is a free radical substitution reaction
CH4 + Br2 → CH3Br + HBr
48. Define Inductive effect with example?
-Inductive effect is an experimentally observable effect of the transmission of charge through a chain of atoms in a molecule.
example:- alkyl, aryl, metals.
49.Write the stability of free radicals based on bond dissociation energy?
- The bottom line is that radicals are electron deficient and that any factor which either helps to donate electron density to the half failed orbital, or to spread that unpaired electron out over a larger volume will stabilize the radical it's called bond dissociation energy.
50. Define Geometrical isomerism with example?
- Geometrical isomerism results from a restriction in rotation about double bonds or about single bonds in cyclic compounds
example:- 2-Butene exists in two spatial arrangements.
51. Write the structure and IUPAC Name - a) Isobutene b) Dimethyl ketone
-a) Isobutene :-
IUPAC Name: 2-Methylprop-1-ene
b) Dimethyl ketone:
IUPAC Name: propan-2-one
52. Write the structure of a)1,3-butsdine b) 2,4,6-tribromoamiline
-a) 1,3-butsdine:
b) 2,4,6-tribromoamiline
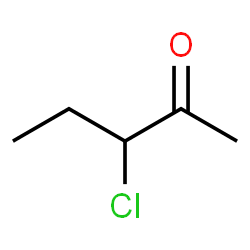
53. Write the structure of -a)2,2 dimethyl propane b) 3-chloro pentanone
- a)2,2 dimethyl propane:
54. Write the structure and IUPAC Name of a) Acetaldehyde b) Acetone?
-a)Acetaldehyde:
IUPAC Name: ethanal
b)Acetone:
IUPAC Name: propan-2-one
55.Write the structure of a) ortho-hydroxy benzoic acid b) 2-methyl cyclopentanone
-a) ortho-hydroxy benzoic acid:
b) 2-methyl cyclopentanone:
56. what is Mesomeric effect?
-The mesomeric effect is defined as the polarity produced in the molecule by the interaction of two π bond and lone pair of electrons present on an adjacent atom.
57. What is Elimination reaction?
- An Elimination reaction is a type of organic reaction in which two substituents are removed from a molecule in either a one or two step mechanism.one step mechanism is known as E1 reaction and two step mechanism is known as E2 reaction.
58. Define Carbanion? Write one method of formation of Carbanion?
-An organic anion in which the negative charge is located on a carbon atom.
- Carbanions are formally derived from neutral organic molecules by removal of positively charged atoms or groups of atom.
59.Define amines? Give the reason why amines are called basic in nature?
- Hydrocarbon derivatives of ammonia are called Amines.
Amines are basic in nature because the presence of lone pair of electron on nitrogen atom of amines makes it basic.
60. What is curtius rearrangement?
-The Curtius rearrangement first defined by Theodor Curtius in 1885, is the thermal decomposition of an acyl azide to an isocyanate with loss of nitrogen gas
61.Why Phenols are acidic in nature?
-Phenol is a very weak acid and the position of equilibrium lies well to the left. Phenol can lose a hydrogen ion because the phenoxide ion formed is stabilized to some extent.
62.What are leaving groups? give example?
-A leaving group is a molecular fragment that departs with a pair of electrons in hetrolytic bond cleavage.
63. Give reason, why carbon tetrachloride has azerodipole moment?
- carbon tetrachloride is non polar molecule because the central carbon atom undergoes SP3 hybridization which results in regular tetrahedral geometry in which all the four C-Cl bond has no net dipole moment.
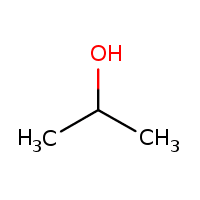
64.Writ the structure and IUPAC Name of a) Methyl formate b)Isopropyl alcohol
-a) Methyl formate
IUPAC Name: Methyl formate
b)Isopropyl alcohol
IUPAC Name:propan-2-ol
65 Give the reason why Trimethyl is less basic than dimethyl amine?
- Dimethyl amine is more acidic than trimethyl amine because due to steric affect electron is not easily available as we known that those bases are more basic which give electron easily and that the reason why dimethyl amine is more basic
66.Write the structure of a) 3-methyl-2-butanone b) 2-Hexanol
-a) 3-methyl-2-butanone
b) 2-Hexanol
67.What is Reimer-timann reaction? Write and example?
- The Reimer-timann reaction is a chemical reaction used for the Ortho -formylation of Phenols.
Example:-Phenol to Salicylaldehyde.
68. What is Hemolytic fission? Give example?
-Hemolytic fission is a chemical bond dissociation of a molecule by a process where each of the fragments retains one of the originally bonded electrons.
example:-alkane and a halogen reacting in the presence of ultra violet light.
69.What is Keto-enol tautomerism? Give example?
-Keto-enol tautomerism refers to a chemical equilibrium between a keto form and enol.
example_ Carbonyl enol- Kenolization.
70. Write the structure and IUPAC Name of a) tert-Butyl chloride b)Formamide
- a) tert-Butyl chloride
IUPAC Name:2-chloro-2-methylpropane
b)Formamide
IUPAC Name: Methanamide
71.What happens when Grignard reagent reacts with ketone?
- Grignard reagent reacts with ketone to give Alcohols
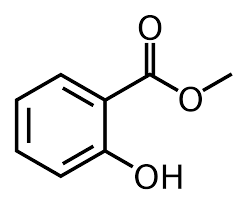
8.Write the structure of a)Methyl salicylate b)m-Dinitro benzene
- a)Methyl salicylate b)m-Dinitro benzene
-:Thank You:-










































0 Comments
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box