
Principal
Half-wave potential
Half-wave potential (E1/2) is a potential at which polarographic wave current is equal to one half of diffusion current (id). In a given supporting electrolyte, the half-wave potential is unique for each element and its different valence states and chemical forms. Observation of a current peak at a specific half-wave potential therefore identifies the chemical species producing the current.

Ilkovic equation
Ilkovic equation is a relation used in polarography relating the diffusion current (id) and the concentration of the depolarizer (c), which is the substance reduced or oxidized at the dropping mercury electrode. The Ilkovic equation has the form
id = k n D1/3m2/3t1/6c
The equation is named after the scientist who derived it, the Slovak chemist, Dionýz Ilkovic 1907-1980)
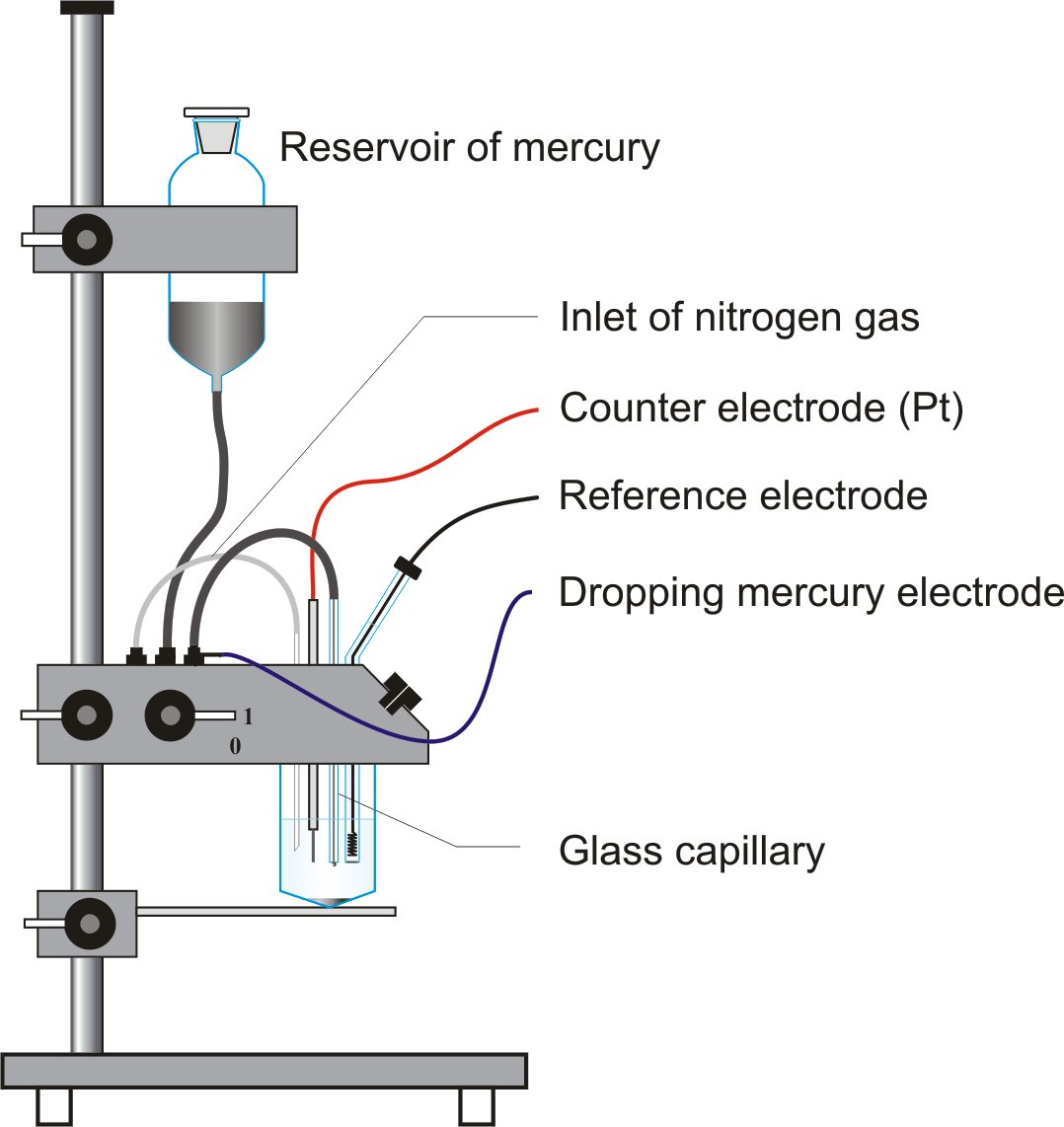
Dropping mercury electrode (DME)
Dropping mercury electrode (DME) is a working electrode arrangement for polarography in which mercury continuously drops from a reservoir through a capillary tube (internal diameter 0.03 - 0.05 mm) into the solution. The optimum interval between drops for most analyses is between 2 and 5 s. The unique advantage to the use of the DME is that the constant renewal of the electrode surface, exposed to the test solution, eliminates the effects of electrode poisoning.
Diagram
Construction
- Dropping mercury electrode is consist of a fine capillary having a bore size ranged from 20 to 50μ and 10 to 15 cm long.
- It is connected to a mercury reservoir by a rubber tubing .
- The height of reservoir is adjusted to set the drop time as required, i.e. 1-5 seconds.
- Drop time is the time required to from every fresh drop of mercury capillary.
- Inside the tubing wire contact is made where mercury flows.
Working
- Dropping mercury electrode is a polarizable electrode and can act as both anode and cathode.
- Generally it is used as cathode but in some experiment it is used as anode by reversing polarity.
- The pool of mercury act as a counter electrode, i.e. anode if DME is cathode or anode if DME is anode.
- To the analytic solution supporting electrolytic like KCl is added .
- pure nitrogen or hydrogen gas is bubbled through the solution to expel out the dissolved oxygen.
- if analyze solution is composed of cadmium than cadmium ions are discharged at cathode.
Cd2+ + 2e → Cd - The gradually increasing voltage is applied to the polarographic cell and corresponding value of current to get a current voltage curve.
- The graph is the representation of polarization and apparatus is known as polarograph.
Advantage
- Surface area is reproducible with a given capillary .
- Constant renewal of electrode surface eliminate poisoning effect.
- Mercury forms amalgam with most the metals.
- Surface area of a drop can be calculate from the weight of drop.
Disadvantage
- Surface area of each drop of mercury is never constant.
- Mercury is very poisonous, so careful handling is required.
- It is limited in its voltage range in the positive direction.
Rotating platinum electrode
Construction
- Rotating platinum electrode consist of a about 5mm platinum wire having 0.5 mm diameter below standard mercury seal.
- The copper wire is passed through the 6mm glass tubing ranging from platinum mercury seal to the upper mercury seal by passing through the small hole blown in the stem of the stirrer.
- A wire from mercury seal is connected to the source that apply voltage.
- Tubing is rotated at a constant speed of 600 rpm
Working
Diagram
 Application:
Application:

- polarography is widely used for determining trace metals and drugs having metallic constitutes
- The metals that are estimated are Fe, Mg, Zn, Pb and Cu
- Estimation of both fat solution and water soluble vitamins can be done by using DME





0 Comments
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box